Part A: Technology Enhanced Unit Design
Introduction to the Learning Unit
The learning unit is focused on teaching Training Development Officers on the conduct of program validations. A validation focuses on determining if a training program has prepared members to complete a specific job or task and validations determine the effectiveness and efficiency in which training programs are conducted.
A holistic review of the Training Development Officer Basic Qualification Course – the aim of the course is to prepare member to provide guidance on Canadian Armed Forces education policies and process. The course is focused on providing junior members with the knowledge and skills required to perform an entry-level position.
The Learning Unit
The main purpose of the unit is to provide the learner with an understanding of the validation process. The process of conducting a validation is based on four steps – Plan, Design, Interpret and Report. Each of the steps is required to be completed in order to ensure the success of a validation study. The Conducting Training Program Validations Unit is made up of five lessons:
- Introduction to Program Validations
- Planning a Validation
- Design a Validation Survey
- Interpret Validation Data
- Report Validation Results
Unit Objective
The Unit Objective is as follows:
- Upon successful completion of the unit, the student will be able to conduct training program validations to the expected level of an entry-level Training Development Officer.
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives are as follows:
- The student will be able to explain the validation process including the steps of conducting validation studies and the purpose of validation studies.
- The student will be able to plan a validation study by providing key milestones and scheme of manoeuvres.
- The student will design a validation survey based on a specific set of tasks or job.
- The student will interpret validation study data by providing a thorough analysis of the findings and developing interpretations.
- The student will report the validation study results by articulating the results and recommendations.
Lesson Mapping Chart – Learning Objectives, Students Outcomes, Activities, and Assessments

An Introduction to the Unit
Validation of Training Programs: Validation is the final cycle of the quality control process as described by the CFITES Process. Validations are used in order to determine if the individual training program is meeting the operational requirements. It is important to understand that validations are normally conducted 6-18 months after a training program has been completed by a student. Validations are seen as an important element in the training cycle. Ineffective training that does not prepare members to complete tasks and jobs could have a negative impact on operations, could cause injury, and could have a negative impact on the financial side of training.
There are Unit will focus on the process of conducting validations. The processes are: Planning, Designing, Interpreting, and Reporting
The entire process of validating a training program can be summed up by the following:
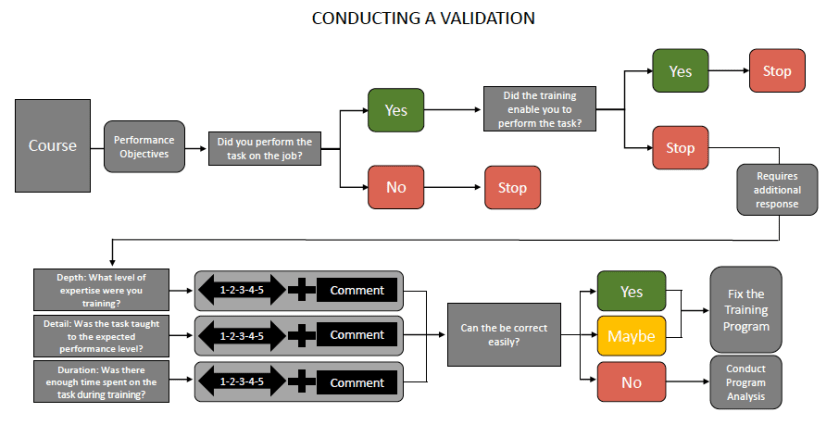
The goal of the unit is to give students knowledge regarding how to conduct a validation study and give the students the opportunity to put their learning into action through real-world applications of knowledge and skills.
Integrated Learning Theories
My personal Learning Theory is based on a combination of a constructivist approach and Bloom’s Taxonomy. The following graphic depicts my personal learning theory:

The concept behind my personal learning theory is based on developing a foundational understanding of a subject, topic or material. Once a foundational understanding has been established, the learner should interact with the subject-matter. The learner needs to interact with the material through an experience that allows the learner to connect with their personal learning. The learner should be able to apply the learning to different situations and scenarios, broaden their depth of learning. Finally, the learner should be able to create solutions to issues or situations based on their newly gained knowledge and skills. At the beginning stages of learning – the learner interaction will be focused on learner-teachers-content. As the learner progresses, the learner will have a more learner-content interaction. As the learner progresses through the model, the level of reflection should increase. The learner should be given opportunities for increased reflection that will allow for an increased learning experience.
The unit design includes the integration of different learning theories including a constructivist approach, the application of Bloom’s Taxonomy and the ARCS model of motivational design. The main purpose of the unit is to teach the student the skill and knowledge of conducting a validation study. The unit should prepare the students to immediately conduct validation and the selection of the different learning approaches and models were picked because of their abilities to teach knowledge and practical skills.
A constructivist approach to learning allows students to be active in the learning process. The use of a constructivist approach in this unit will allow the learners to discovery the validation study process through activities that relate to the real-world application. The activities build upon each other, building the unit in this fashion will allow for constructing knowledge through the application in a realistic manner. The benefit for using a constructivist approach in this unit includes: using real-world and authentic learning experiences, the relevance of the knowledge and skills, the use of formative assessments to provide feedback, and the instructor is facilitating the learning (Carwile, 2007).
Blooms Taxonomy was considered during the unit. The assignments and assessments were the main focus for applying and orientating the unit to Bloom’s Taxonomy. The knowledge and comprehension stages of the taxonomy will be achieved throughout the unit. During the first lesson, the student’s understand and comprehension will be evaluated during the blog post. Students will be completing a validation plan and survey design – these activities achieve the application level as students are applying their learning to complete validation products. The recommendation and reporting activities will achieve the analysis level of the taxonomy, as the learners will have logically developed recommendations based on survey findings. The reporting of these findings will require a deeper analysis of the entire validation study. Throughout the unit, the learner will evaluate their own work as well as they will conduct peer-to-peer reviews on the blog posts. The activities and assessments will allow the student to gain a deep appreciation for the subject and will be able to build a deeper and more meaningful learning experience
The ARCS model was considered during the design of the unit. The main reason for considering the use of the ARCS model was to create and maintain a high level of motivation. Building the unit around providing students with immediately applicable skills meets the requirements of the ARCS model as it grabs the attention of the learner through real-world examples that are included in the unit. The relevance of the material is relatable as it is applicable to the student’s job; the unit allows for the learner to pick their own content when building their assessments. Through formative and summative assessments, feedback will help to build the confidence of the learner. After the student completes the unit, the student now has the skill and knowledge to apply the lessons learned in order to complete a validation study. The immediate application of skill and knowledge will provide a high level of learner satisfaction (Pappas, 2015).
The Technology
The inclusion of web 2.0 technologies in the unit maps to the benefits of the chosen technologies. There are four main benefits that map to the best practices. The best practices include: facilitating learning, fostering interaction, collaborative problem solving and providing prompt feedback (Odom, 2005). The use of a website in the unit facilitates learning through the use of a pre-authorized site that uses graphics and examples. Each student will have a blog site where there can author there own content and the content will be shared. The use of the technologies in the unit allows for the fostering of interaction. As the students progress in the unit, they will be continuously sharing their work through blog posts. The blog posts will allow the learners to share their experiences and will foster interaction. Within the unit, the analysis of data activity will be conducted in pairs. Google Docs will be used for the activity as it allows for collaborative problem solving to be conducted in real time. The web 2.0 tool, Google Docs, will allow for the pairings to interact in real-time and will allow for the collaborative analysis of data. Feedback will be prompt throughout the unit. The instructor can provide feedback throughout the blog posts and assignments. The feedback will allow the students to understand their successes and areas to improve. Web 2.0 tools are integrated into the unit and will add to the learning experience for all involved in the unit.
The technology in the unit is very practical in nature and has a positive impact of the learner through the real world applications. As an online learner, knowing that there is a practical use for a piece of technology only increases the motivation within a lesson or unit. Building this unit around a practical job skill, it only made sense to use the technology that goes hand-in-hand with the practical application. The foundational understand and conduct of validation studies is at the core of the unit. The technology only complements the learning and provides additional tools for completing the validation studies.
The rationalization for using the technologies in the unit is based on the real-world application of the technologies. The use of the technologies in the unit allows for the learner to become familiar with the programs that will be used on the job. The learner will gain confidence in their abilities to manipulate the technology. The technology that will be used in the unit includes blogging sites, InfoPath forums, survey templates, word processing and uploading video sites. Incorporating blogging sites and reflective technologies allow for the development of a learning environment. The development of a productive learning environment can allow the learner to build his or her own learning. A positive online learning environment can incorporate various amount of content and content types. An effective online learning environment can be inclusive of all types of students. The online learning environment needs to include flexibility built into it. Anderson (2008) states that effectively designed online learning constructs a “learning environment that is simultaneously learner-centred, content-centred, community-centred, and assessment-centred. There is no single best media of online learning” (p. 21). An online learning model should be able to be made up of multiple different learning environments.
Using web 2.0 tools in an online course allows for the development of a learning community. According to Abdelmalak (2015), “To develop a successful online course, many scholars suggest that building and sustaining an online learning community is crucial and necessary”. Students who are at a distance can have a feeling of being isolated. The learning community should not just be a social community but should have the ability to “convey knowledge about the content and for the community to collaboratively make meaning from that content” (Abdelmalak, 2015). The development of an online learning community through the use of web 2.0 tools can improve the learner’s experience
Online learning can have many different barriers that can impede the quality of learning. The two many barriers are distance and time as the learners will be located across the country and will be in different time zones. Also, individuals will have day-to-day responsibilities that will not allow for synchronous learning. The use of web 2.0 tools and the construction of the unit allows the learners to connect to the content, peers and instructor. The students will have the ability to connect learning through the provided technology. They will be able to develop their own meaningful learning through their interactions with the material, peers and the instructor. The technology used will close the gap in distance and time, as it will provide the students with a positive learning environment. Also, the use of the web 2.0 technology will allow for individual reflection through the lessons and assignments.
References
Abdelmalak, M. (2015). Web 2.0 Technologies and Building Online Learning Communities: Students’ Perspectives. Assiut University, Egypt.
Anderson, T. (2008). Toward a Theory of Online Learning. In Theory and Practice of Online Learning. Retrieved from https://ustpaul.ca/uploadfiles/DistanceEducation /TOWARDS_A_THEORY_OF_ONLINE_LEARNING.pdf
Carwile, J. (2007). A Constructivist Approach to Online Teaching and Learning. Inquir. 12(1), p. 68-73. Retrieved from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ833907.pdf
Iversity. (2017). Effective Online Learning Covers All Steps of Bloom’s Taxonomy. Rethinking Online Education. Retrieved from https://iversity.org/blog/effective-onlinelearningblooms-taxonomy/
Odom, L. (2005). Mapping web 2.0 benefits to known best practices in distance education. Research Gate.
Pappas, C. (2015). Instructional Design Models And Theories: Keller’s ARCS Model Of Motivation. eLearning Industry. Retrieved from https://elearningindustry.com/arcs model-of-motivation